728x90
병합 정렬(merge sort)는?
- 재귀용법을 활용한 정렬 알고리즘
1. 리스트를 반으로 잘라 비슷한 크기의 두 부분 리스트로 나눈다.
2. 각 부분 리스트를 재귀적으로 합병 정렬을 이용해 정렬한다.
3. 두 부분 리스트를 다시 하나의 정렬된 리스트로 합병한다.
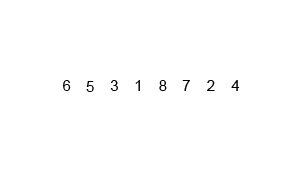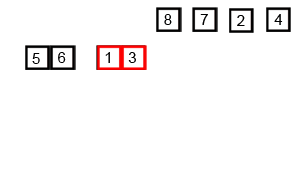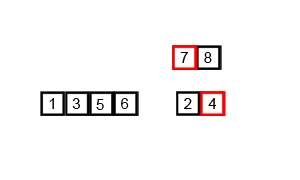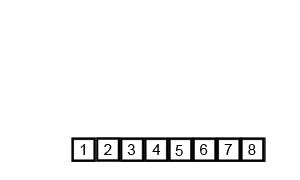
알고리즘 이해
- 데이터가 4개 일 때
data_list = [1, 8, 4, 3]
먼저 [1, 8], [4, 3]으로 나누고 다시 앞 부분은 [1], [8]로 나누고 다시 정렬해서 합침 [1, 8]
다음 [4, 3] 는 [4], [3]으로 나누고 다시 정렬해서 합침 [3, 4]
[1, 8]과 [3, 4]를 합침
- 1 < 3 이니 [1]
- 8 > 3 이니 [1, 3]
- 8 > 4 이니 [1, 3, 4]
- 8만 남았으니 [1, 3, 4, 8]
알고리즘 구현
- mergesplit 함수 만들기
- 만약 리스트 갯수가 한개이면 해당 값 리턴, 그렇지 않으면 리스트를 앞 뒤 2개로 나눔
- left = mergesplit(앞)
- right = mergesplit(뒤)
- merge(left, right)
- marge 함수 만들기
- 리스트 변수 하나 만들기 (sorted)
- left_index, right_index = 0
- while left_index < len(left) or right_index < len(right):
만약 left_index나 right_index가 이미 left 또는 right리스트를 다 순회했다면 그 반대쪽 데이터를 그대로 넣고 해당 인덱스 1증가
if left[left_index] < right[right_index]:
sorted.append(left[left_index])
left_index += 1
else:
sorted.append(right[right_index])
right_index += 1
프로그래밍 연습
#데이터리스트를 앞뒤로 자르는 코드 작성해보기
def split_func(data):
medium = int(len(data) / 2)
print (medium)
left = data[:medium]
right = data[medium:]
print
split_func([1, 5, 3, 2, 4])
"""출력
2
[1, 5], [3, 2, 4]
"""
left, right리스트 변수의 데이터 수가 한 개에서 여러 개가 될 수 있을 때 작성해보기
- sorted_list 리스트 변수 선언
- left_index, right_index를 0으로 초기화 하기
- while left_index < len(left) or right_index < len(right) 이면
- 만약 left_index >= len(left)이면, sorted_list에 right[right_index]를 추가하고 right_index 값을 1증가
- 만약 right_index >= len(right)이면, sorted_list에 left[left_index]를 추가하고 left_index값을 1증가
- 만약 left[left_index] < right[right_index]이면, sorted_list에 left[left_index]를 추가하고 left_index값을 1증가
- 위 세가지가 아니면 sorted_list에 right[right_index]를 추가하고 right_index값을 1증가
def marge(left, right):
merged = list()
left_point, right_point = 0, 0
#left/right 둘 다 있을 때
while len(left) > left_point and len(right) > right_point:
if left[left_point] > right[right_point]:
merged.append(right[right_point])
right_point += 1
else:
merged.append(left[left_point])
left.point += 1
#left데이터가 없을 때
while len(left) > left_point:
merged.append(left[left_point])
left_point += 1
#right 데이터가 없을 때
while len(right) > right_point:
merged.append(right[right_point])
right_point += 1
return merged
총 코드
def merge(left, right):
merged = list()
left_point, right_point = 0, 0
#left/right 둘 다 있을 때
while len(left) > left_point and len(right) > right_point:
if left[left_point] > right[right_[point]:
merged.append(right[right_point])
right_point += 1
else:
merged.append(left[left_point])
left_point += 1
#left데이터가 없을 때
while len(left) > left_point:
merged.append(left[left_point])
left_point += 1
#right데이터가 없을 때
while len(right) > right_point:
merged.append(right[right_point])
right_point += 1
return merged
def mergesplit(data):
if len(data) <= 1:
return data
medium = int(len(data) / 2)
left = mergesplit(data[:medium])
right = mergesplit(data[medium:])
return merge(left, right)import random
data_list = random.sample(range(100), 10)
mergesplit(data_list)
#출력결과 [8, 12, 24, 40, 47, 70, 81, 87, 92, 96]'IT개발 > 알고리즘, 우리 친해지자!' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 알고리즘 : 순차탐색(Sequential Search) (0) | 2021.09.11 |
|---|---|
| 알고리즘 : 이진 탐색(Binary Search) (0) | 2021.09.06 |
| 알고리즘 : 퀵 정렬(Quick sort) (0) | 2021.08.30 |
| 알고리즘 : 동적계획법(Dynamic Programming)과 분할정복(Divide and Conquer) (0) | 2021.08.28 |
| 알고리즘 : 재귀 용법(recursive call) (0) | 2021.08.26 |



